Baby Growth Stages
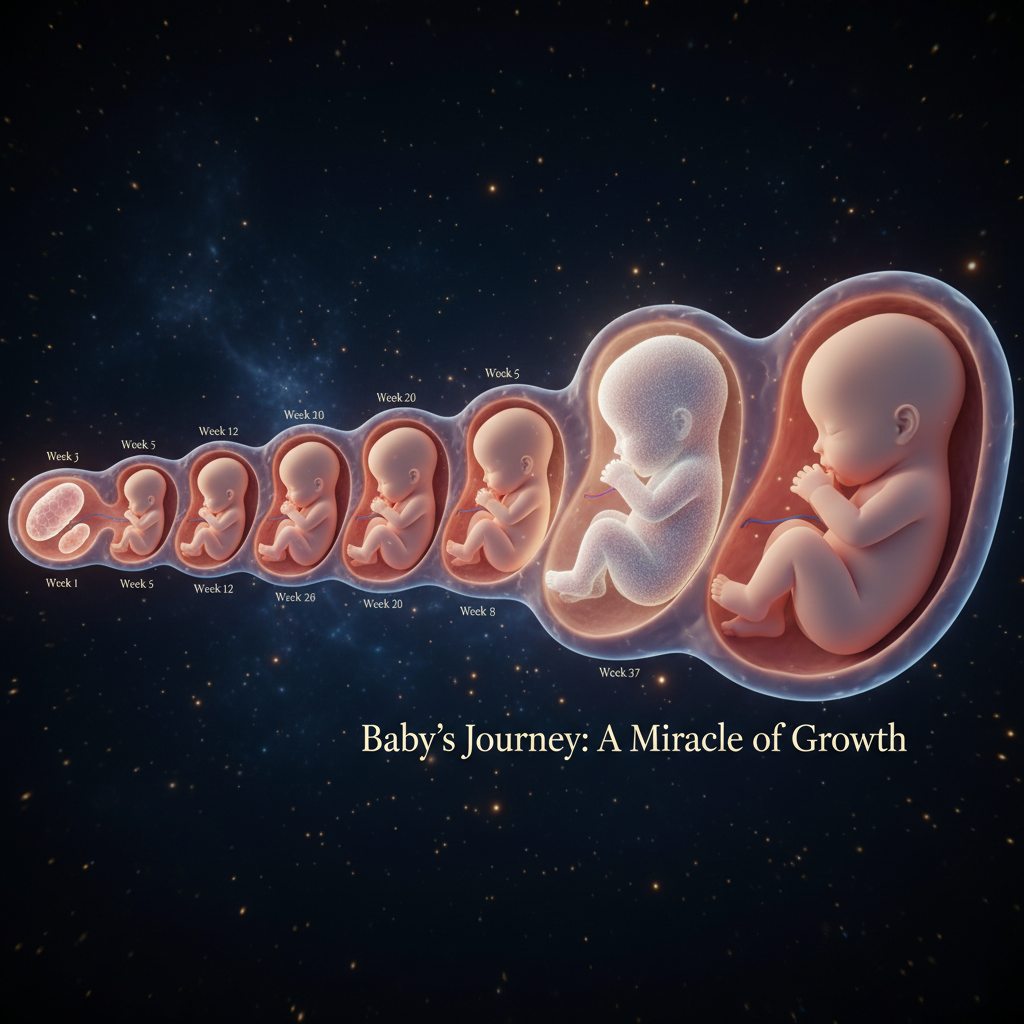
Understanding the stages of baby growth during pregnancy helps you monitor development and prepare for parenthood. This guide outlines key developmental milestones across the three trimesters, from conception to birth. Always consult a healthcare provider to track your baby’s growth and address any concerns, especially for high-risk pregnancies.
First Trimester (Weeks 1–12)
The first trimester is critical for foundational development as the embryo forms major organs and systems.
-
Weeks 1–4:
-
Fertilization occurs, and the embryo implants in the uterine lining.
-
The neural tube (future brain and spinal cord) begins forming.
-
The heart starts developing and may begin beating by week 4 (detectable by ultrasound around week 6).
-
Size: By week 4, the embryo is about the size of a poppy seed (~1–2 mm).
-
-
Weeks 5–8:
-
Major organs (e.g., brain, heart, lungs) and limbs start forming.
-
Facial features (eyes, nose, mouth) begin to develop.
-
The heart beats regularly, and blood circulation starts.
-
Size: By week 8, the embryo is about the size of a raspberry (~1.5–2 cm).
-
-
Weeks 9–12:
-
The embryo is now called a fetus.
-
Fingers, toes, and facial features become more defined.
-
Organs like the liver and kidneys start functioning minimally.
-
Genitals begin forming, though not always visible on ultrasound.
-
Size: By week 12, the fetus is about the size of a plum (~5–6 cm).
-
-
Key Maternal Actions:
-
Take 400–800 mcg of folic acid daily to support neural tube development.
-
Schedule a prenatal visit to confirm pregnancy and monitor early growth.
-
Track symptoms like nausea or fatigue in a notebook or digital reminder system to discuss with your healthcare provider.
-
Second Trimester (Weeks 13–26)
The second trimester focuses on rapid growth, organ maturation, and the fetus becoming more active.
-
Weeks 13–16:
-
The fetus develops hair, nails, and skin.
-
Muscles and bones strengthen, enabling small movements.
-
The digestive system and lungs continue maturing.
-
Size: By week 16, the fetus is about the size of an avocado (~11–14 cm).
-
-
Weeks 17–20:
-
The fetus begins to kick and move, often felt by the mother (around weeks 18–20, known as quickening).
-
A protective coating (vernix) forms on the skin.
-
Heartbeat becomes stronger and detectable via Doppler.
-
Gender may be identifiable via ultrasound (if desired).
-
Size: By week 20, the fetus is about the size of a banana (~25 cm).
-
-
Weeks 21–26:
-
Eyes open, and the fetus responds to light and sound.
-
Brain development accelerates, supporting early sensory functions.
-
Lungs develop air sacs, though not yet ready for breathing.
-
Size: By week 26, the fetus is about the size of a zucchini (~35 cm).
-
-
Key Maternal Actions:
-
Monitor fetal movements daily (e.g., aim for 10 kicks in 2 hours by week 28) and note patterns in a log.
-
Maintain a balanced diet rich in iron, calcium, and omega-3s to support growth.
-
Attend regular prenatal checkups to track development via ultrasounds or measurements.
-
Third Trimester (Weeks 27–40)
The third trimester focuses on final growth, organ refinement, and preparation for birth.
-
Weeks 27–32:
-
The fetus gains significant weight, adding fat layers for temperature regulation.
-
Brain and nervous system mature, supporting reflexes like grasping.
-
Bones harden, though the skull remains soft for delivery.
-
Size: By week 32, the fetus is about the size of a pineapple (~43–45 cm).
-
-
Weeks 33–36:
-
The fetus moves into a head-down position (in most cases) to prepare for birth.
-
Lungs mature, producing surfactant to aid breathing after birth.
-
Immune system strengthens, receiving antibodies from the mother.
-
Size: By week 36, the fetus is about the size of a honeydew melon (~46–48 cm).
-
-
Weeks 37–40:
-
The fetus is considered full-term by week 37 and ready for birth.
-
Organs are fully developed, though the brain and lungs continue maturing post-birth.
-
Movements may slow due to limited space, but kicks remain detectable.
-
Size: By week 40, the fetus is about the size of a small pumpkin (~50–52 cm, 6–9 lbs).
-
-
Key Maternal Actions:
-
Create a birth plan outlining delivery preferences, but remain flexible for medical needs.
-
Pack a hospital bag with essentials for you and the baby (e.g., clothing, toiletries).
-
Continue tracking fetal movements and report any significant decreases to your healthcare provider.
-
Benefits of Tracking Baby Growth
-
Informed Monitoring: Understanding milestones helps you recognize normal development and flag concerns early.
-
Emotional Connection: Tracking growth fosters bonding with your baby through awareness of movements and milestones.
-
Better Preparation: Aligns maternal health practices (e.g., nutrition, checkups) with fetal needs.
Practical Tips
-
Tracking Tools: Use a notebook, calendar, or digital reminder system to log prenatal appointments, fetal movements, and maternal symptoms. Note key milestones (e.g., first kicks, ultrasound findings).
-
Nutrition: Eat a balanced diet with folate-rich foods (e.g., leafy greens), calcium sources (e.g., dairy or fortified alternatives), and omega-3s (e.g., fish, nuts) to support fetal growth.
-
Fetal Movement Monitoring: Start tracking kicks in the second trimester. Use a simple log to record daily activity patterns and report changes to your healthcare provider.
-
Prenatal Checkups: Attend regular appointments to monitor growth via ultrasounds, fundal height measurements, or Doppler heart rate checks.
-
Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or prenatal yoga to support maternal and fetal well-being.
-
High-Risk Pregnancies: If you have conditions like hypertension or a history of preterm birth, discuss more frequent monitoring (e.g., additional ultrasounds) with your healthcare provider.
Actionable Next Steps
-
Today: Choose a tracking tool to log your due date and upcoming prenatal appointments.
-
This Week: Begin taking 400–800 mcg of folic acid daily (first trimester) and schedule your first prenatal visit.
-
Ongoing: Track fetal movements (second trimester onward) and attend regular checkups to monitor growth milestones. Consult your healthcare provider if you notice irregularities (e.g., reduced movements, unusual symptoms).
Related Articles

Week 6 - Limb Buds Appear

Period calculator
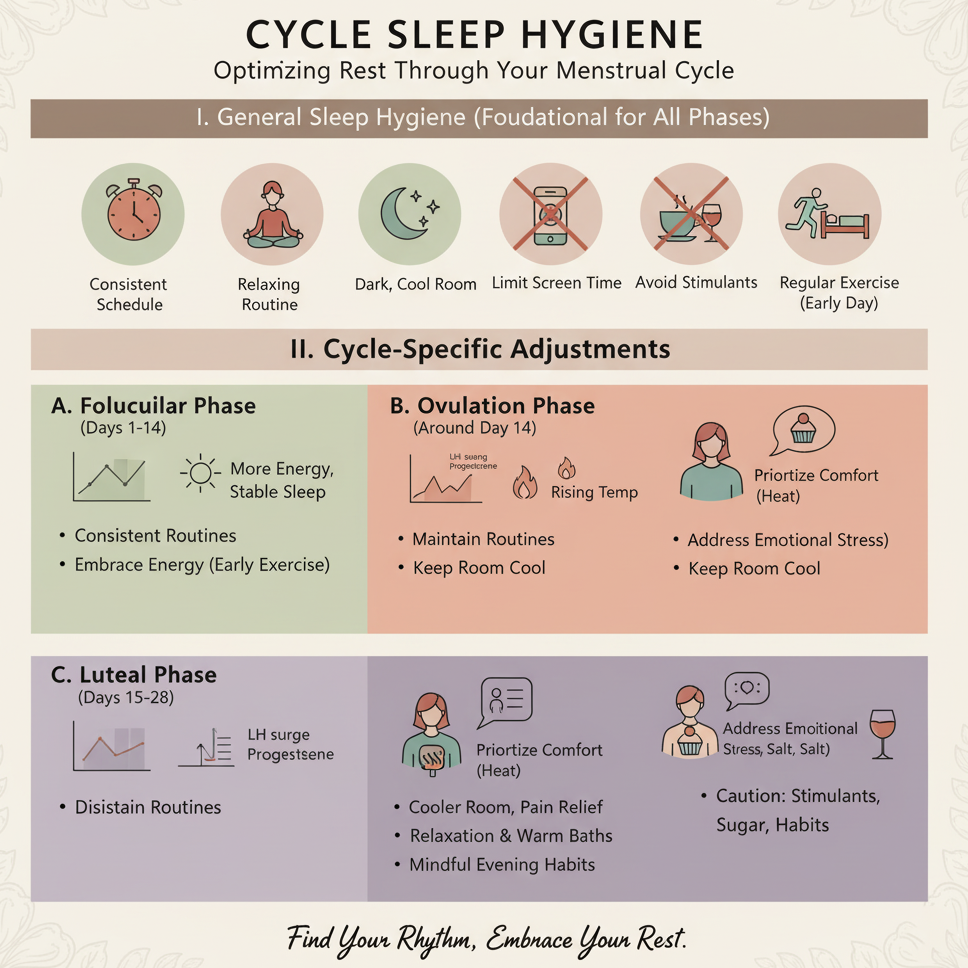
Cycle Sleep Hygiene

Week 25 - Brain Growth Spurt

Week 4 - Neural Tube Development

Week 23 - Skin Thins

Week 16 - Mid-Pregnancy Milestone

Week 20 - Halfway Point