Symptom Alert System

A symptom alert system helps expectant parents monitor pregnancy-related symptoms, distinguish normal changes from potential concerns, and take timely action to ensure maternal and fetal health. By tracking symptoms and knowing when to seek medical advice, you can enhance safety and peace of mind throughout pregnancy. Always consult a healthcare provider promptly for concerning symptoms or if you have high-risk factors.
1. Set Up a Tracking Tool
-
Action: Use a notebook, calendar, or digital reminder system to log daily symptoms, their frequency, severity, and duration.
-
What to Track:
-
Common symptoms (e.g., nausea, fatigue, breast tenderness).
-
Fetal movement patterns (second and third trimesters).
-
Potential warning signs (e.g., bleeding, severe pain, reduced fetal movement).
-
-
Purpose: Creates a record to identify patterns and share with your healthcare provider for accurate assessment.
2. Understand Normal Pregnancy Symptoms
Familiarize yourself with typical symptoms by trimester to distinguish normal changes from concerning ones:
-
First Trimester (Weeks 1–12):
-
Nausea and vomiting (morning sickness), often peaking around weeks 6–9.
-
Fatigue, breast tenderness, and frequent urination.
-
Mild cramping as the uterus expands.
-
-
Second Trimester (Weeks 13–26):
-
Increased energy, though some fatigue may persist.
-
Mild back pain, round ligament pain (sharp, one-sided abdominal discomfort), and nasal congestion.
-
Fetal movements felt around weeks 18–20 (quickening).
-
-
Third Trimester (Weeks 27–40):
-
Shortness of breath, swelling in feet or ankles, and Braxton Hicks contractions (irregular, mild tightening).
-
Increased pelvic pressure as the baby descends.
-
Continued fetal movements, though less intense due to limited space.
-
-
Purpose: Helps you recognize expected symptoms and avoid unnecessary worry.
3. Identify Warning Signs Requiring Immediate Action
Log and act on symptoms that may indicate complications. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience:
-
Any Trimester:
-
Vaginal bleeding or spotting (beyond light spotting in early pregnancy).
-
Severe or persistent abdominal pain or cramping.
-
Severe headaches, dizziness, or vision changes (e.g., blurred vision, spots).
-
Fever above 100.4°F (38°C) or chills.
-
-
Second/Third Trimester:
-
Reduced or absent fetal movement (e.g., fewer than 10 movements in 2 hours after week 28).
-
Sudden swelling in hands, face, or legs, which may signal preeclampsia.
-
Leaking fluid or suspected amniotic fluid (clear or greenish discharge).
-
Persistent vomiting or inability to keep food/fluids down.
-
-
Purpose: Ensures prompt response to potential issues like miscarriage, preterm labor, or preeclampsia.
4. Establish a Monitoring Routine
-
Daily Check-Ins:
-
Record symptoms each morning or evening, noting intensity (e.g., mild, moderate, severe) and triggers (e.g., after eating, during activity).
-
Track fetal movements daily starting in the second trimester (e.g., count kicks during a 2-hour period).
-
-
Weekly Review: Assess symptom patterns (e.g., worsening nausea, new discomfort) and discuss changes at prenatal visits.
-
Purpose: Builds consistency and helps detect subtle changes early.
5. Use Support Tools for Accuracy
-
Fetal Movement Tracking: Use a simple log to record kick counts (aim for 10 movements in 2 hours by week 28). Note the time and context (e.g., after meals).
-
Thermometer: Use a digital thermometer to check for fever if you feel unwell.
-
Ovulation Kits (Pre-Conception): If still trying to conceive, use over-the-counter ovulation predictor kits to confirm fertile windows, which can inform early pregnancy tracking.
-
Purpose: Enhances precision in monitoring and reporting symptoms to your healthcare provider.
6. Involve Your Partner
-
Shared Monitoring: Encourage your partner to help track symptoms or fetal movements, especially during the third trimester.
-
Emergency Plan: Discuss which symptoms require immediate medical attention and ensure both partners know how to contact the healthcare provider.
-
Purpose: Strengthens teamwork and ensures quick action in emergencies.
7. Know When to Seek Medical Advice
-
Routine Concerns: Discuss mild or persistent symptoms (e.g., ongoing nausea, mild swelling) at regular prenatal visits.
-
Urgent Concerns: Call your healthcare provider immediately for warning signs (e.g., bleeding, severe pain, reduced fetal movement).
-
High-Risk Pregnancies: If you have conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or a history of preterm birth, consult your provider sooner for any unusual symptoms.
-
Purpose: Ensures timely intervention to protect maternal and fetal health.
Benefits
-
Early Detection: Identifies potential complications before they escalate.
-
Reduced Anxiety: Clarifies normal vs. concerning symptoms, fostering confidence.
-
Empowered Care: Equips you to communicate effectively with your healthcare provider.
Practical Tips
-
Tracking Tools: Use a paper notebook or phone-based reminder to log symptoms daily. Include date, time, symptom type, and severity (e.g., “mild nausea after breakfast”).
-
Fetal Movement Monitoring: Start kick counts in the second trimester. Choose a consistent time (e.g., after dinner) when the baby is active. Report significant decreases to your provider.
-
Symptom Journal: Note triggers (e.g., foods, stress) and patterns to identify manageable causes (e.g., dietary adjustments for nausea).
-
Stress Management: Practice 10-minute daily relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, meditation) to reduce stress, which can amplify symptoms.
-
Emergency Contacts: Keep your healthcare provider’s contact information and a nearby hospital’s number easily accessible.
-
High-Risk Monitoring: If high-risk, discuss a tailored symptom alert plan with your provider, including more frequent checkups or specific symptoms to watch.
Actionable Next Steps
-
Today: Select a tracking tool and begin logging daily symptoms and pregnancy milestones.
-
This Week: Familiarize yourself with normal vs. warning signs by trimester and create an emergency contact list.
-
Ongoing: Track fetal movements (second trimester onward) and review symptoms weekly. Contact your healthcare provider immediately for any warning signs.
Related Articles

Normal Period Flow

Week 10 - Fingernails Form

Week 38 - Organ Maturation

Week 14 - Bones Harden

Revolutionizing Menstrual Health Management

Week 11 - Gender Differentiation
Week 18 - Hearing Develops
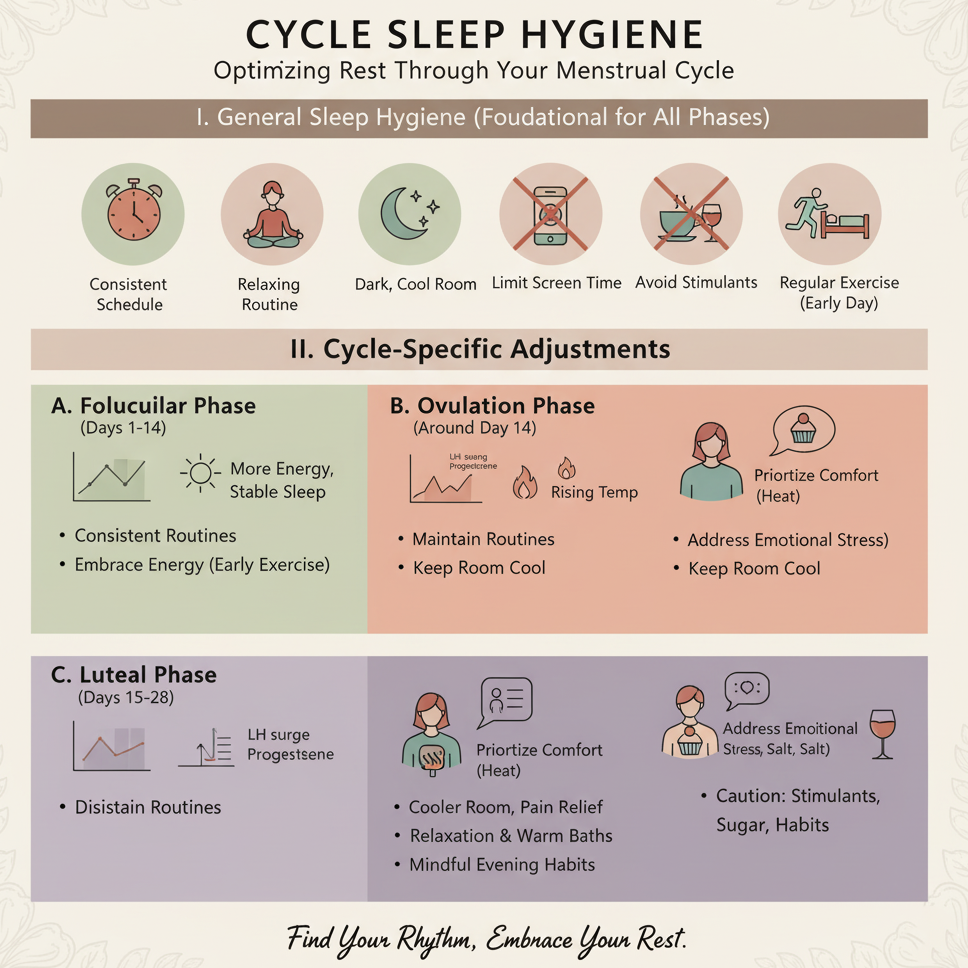
Cycle Sleep Hygiene